Mouse VEGF 164AA Recombinant (E.Coli)
Categories: PDGF familyPDGF familyRecombinant Mouse Cytokines$70.00 – $3,500.00
Description
Accession
Q00731
Source
Optimized DNA sequence encoding Mouse Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 164 mature chain was expressed in Escherichia Coli.
Molecular weight
Native mouse VEGF-165 is generated by the proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and propeptide, the molecule has a calculated molecular mass of approximately 20kDa. Recombinant Vascular endothelial growth factor is a disulfide-linked homodimer protein consisting of 2x165 amino acid residue subunits, and migrates as an approximately 40kDa protein under non-reducing and as 20kDa under reducing conditions in SDS-PAGE.
Purity
>95%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
The ED(50) was determined by the dose-dependent proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and was found to be in the range of.0-4.0 ng/ml.
Protein Sequence
MNFLLSWVHW TLALLLYLHH AKWSQAAPTT EGEQKSHEVI KFMDVYQRSY CRPIETLVDI FQEYPDEIEY IFKPSCVPLM RCAGCCNDEA LECVPTSESN ITMQIMRIKP HQSQHIGEMS FLQHSRCECR PKKDRTKPEN HCEPCSERRK HLFVQDPQTC KCSCKNTDSR CKARQLELNE RTCRCDKPRR
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Recombinant mouse VEGFwas lyophilized from.2 μm filtered PBS solution, pH7.0.
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers.
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at2° -8° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
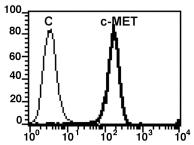
Interactor
P35969
Biological Process
Biological Process
Molecular function
Molecular function
Molecular function
Methods
Culture of Mouse Endothelial Cells
- The MAEC line was a kind gift from Dr Hiroko Inoue, Tsurumi University School of Dental Medicine, Japan.
- The cell line was established from p53-deficient mouse aortas
in vitro. Cells were grown in Medium 199 with 5% FBS, 1 U/ml of heparin sodium and 5 ng/ml of murine VEGF , at 37°C, 5% CO2. - Media was changed every 3–4 days.
Culture of Mouse Endothelial Cells
- The MAEC line was a kind gift from Dr Hiroko Inoue, Tsurumi University School of Dental Medicine, Japan.
- The cell line was established from p53-deficient mouse aortas
in vitro. Cells were grown in Medium 199 with 5% FBS, 1 U/ml of heparin sodium and 5 ng/ml of murine VEGF , at 37°C, 5% CO2. - Media was changed every 3–4 days.
Induction of 2nd iPSCs
- All isolated somatic cells were cultured in the presence of Dox (2 ug/ml) for induction of 2nd iPSCs.
- Fibroblasts and hematopoietic cells were cultured in ES/iPSC medium.
- FLCD45 were cultured in the presence of 10 ng/ml human TPO, 10 ng/ml mouse EPO, 10 ng/ml mouse IL-3, 10 ng/ml mouse IL-6, 10 ng/ml mouse Flt3 ligand, 10 ng/ml mouse GM-CSF, 10 ng/ml mouse VEGF and 50 ng/ml mouse SCF .
- HSCs, HPCs and MPs were cultured in the presence of 10 ng/ml human TPO, 10 ng/ml mouse IL-3, 10 ng/ml mouse IL-6 and 10 ng/ml mouse Flt3 ligand .
- Macrophages were cultured in the presence of 5 ng/ml M-CSF .
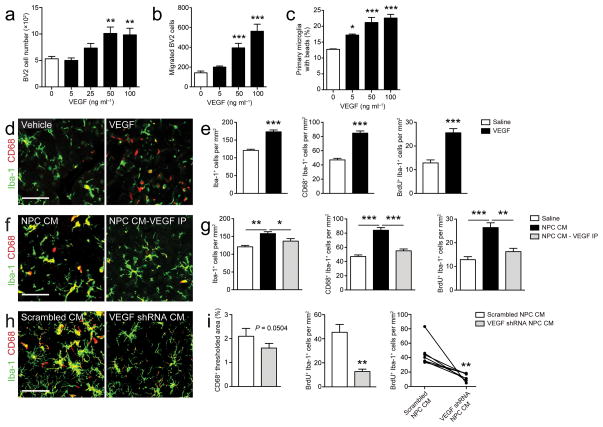
Neural progenitor cell-secreted VEGF is necessary and sufficient for the regulation of microglia (a–b) VEGF regulates microglia in vitro.
- Microglia treated with recombinant VEGF show increased proliferation (a), chemotaxis (b), and phagocytosis (c) (n = 3–6 wells/condition).
Primary Culture of Epicardial Cells and Cardiomyocytes
- Primary epicardial cells were cultured in 10% FBS/MEM containing recombinant soluble factors, such as TGFβ1 (10 ng/ml&systems), FGF2 (100 ng/mloche), , , , , PGF-BB (100 ng/ml) or retinoic acid (1 µmol/l), for 3 days.
- The soluble factors were added on the day of heart removal.
- The medium was replaced daily.
- For western blot analysis, cells were treated with TGFβ1 for 2 days, beginning on the day following heart removal, at a final concentration of 1 ng/ml.
Cells
- Human umbilical vein ECs (Type Tissue Collection) were seeded in sparse (5,000 cells per cm2) or confluent (50,000 cells per cm2) conditions.
- HUVECs starved in medium'>MV2 medium with 1% FCS for 2 h-overnight were stimulated with 20 ng ml−1 of mouse VEGF-A164 , 200 ng ml−1 of COMP-Angiopoietin-1 (COMP-Ang1)−1.
- PAE cells expressing human VEGFR2 (PAE/VEGFR2 (ref.
Matrigel angiogenesis assay in vivo
- C57BL/6 mice background (8 weeks old) were subcutaneously (s.c.) flank-injected with 600 µl of matrigel supplemented with VEGF (100 ng/ml) and heparin .
- The negative controls contained heparin alone.
- Each group consisted of four animals.
- After seven days, mice were sacrificed and matrigel plugs were extracted.
- The angiogenic response was evaluated by macroscopic analysis of the plug at autopsy and by measurement of the hemoglobin content within the pellet of matrigel.
- Hb was mechanically extracted from pellets reconstituted in water and measured using the Drabkin method by spectrophotometric analysis at 540 nm.
- The values were expressed as optical density (OD)/100 mg of matrigel.
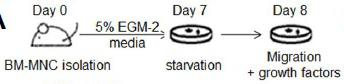
Human ES cell culture and differentiation
- Human H1, H9 and UCLA1-6 (UCLA stem cell core) [–1 bFGF .
- EBs were differentiated according to previous reports with minor modification [
μ M Y27632 (Rho kinase inhibitor IV, EMD Chemicals), 3 ng ml−1 Activin A , 5 ng ml−1 bFGF, 10 ng ml−1 BMP4 and 5μ M IWR-1 (EMD Chemicals), for the first 4 days. - EBs were then cultured in StemPro 34 supplemented with 10 ng ml−1 bFGF, 5 ng ml–1 vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and 5
μ M IWR-1 for 5 additional days before plating onto elastic substrates. - Usage of all human ES cell lines is approved by the UCLA Embryonic Stem Cell Research Oversight (ESCRO) Committee and the Institutional Review Boards (IRB, approval #2009-006-04).
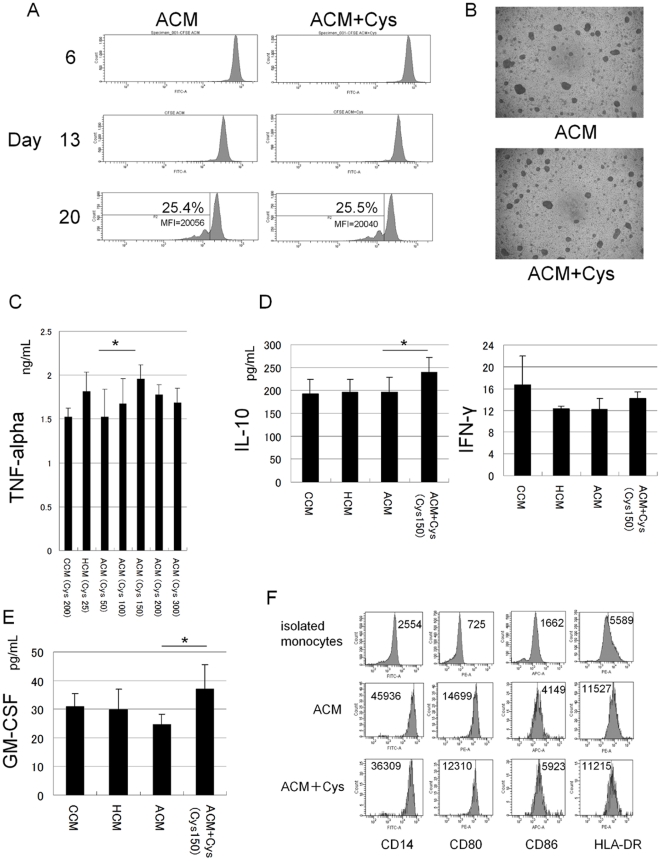
Derivation and characterization of iECs
- iECs were derived using a three-dimensional approach with modifications .
- Briefly, to initiate differentiation, iPSCs were cultured in ultra-low, non-adhesive dishes to form embryoid body (EB) aggregates in EBM2 media in the absence of leukemia inhibitor factor (LIF).
- After 4 days of suspension culture, the EBs were reattached onto 0.2% gelatin-coated dishes and cultured in medium'>EBM2 medium supplemented with VEGF-A165 (50 ng/mL).
- After 3 weeks of differentiation, single cell suspensions were obtained using a cell dissociation buffer and labeled with APC-conjugated CD31 (e) and PE-conjugated CD144 anti-mouse antibodies.
- iECs were purified by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) of CD31+CD144+ population.
- iECs were maintained in EBM2 media supplemented with recombinant murine vascular endothelial growth factor (50 ng/ml).