Mouse Interleukin-7 Recombinant
Categories: HematopoietinsIL-2 familyRecombinant Mouse Cytokines$70.00 – $4,700.00
Description
Accession
P10168
Source
Optimized DNA sequence encoding Human Interleukin-7 mature chain was expressed in Escherichia Coli.
Molecular weight
Native Mouse IL-7, generated by the proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and propeptide, the molecule has a calculated molecular mass of approximately kDa. Recombinant mouse IL-7 is a monomeric protein consisting of amino acid residue subunits. Recombinant IL-7 migrates as an approximately kDa protein under non-reducing and reducing conditions in SDS-PAGE.
Purity
>95%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
The ED(50) dose-dependent stimulation of the proliferation of murineE8 cells is <.1 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of >4 x units/mg.
Protein Sequence
MFHVSFRYIF GIPPLILVLL PVTSSECHIK DKEGKAYESV LMISIDELDK MTGTDSNCPN NEPNFFRKHV CDDTKEAAFL NRAARKLKQF LKMNISEEFN VHLLTVSQGT QTLVNCTSKE EKNVKEQKKN DACFLKRLLR EIKTCWNKIL KGSI
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Recombinant Interleukin-7 was lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in.5% glycine,.5% sucrose,.01% Tween80, mM Glutamic acid, pH.5.
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers.
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at2° -8° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Molecular function
Molecular function
Methods
T cell activation assay
- Stromal cells:24-well 1×104 stromal cells from lines were seeded in complete RPMI and after overnight culture irradiated with 1000rad.
- Initially, experiments with non-irradiated or irradiated pLN2 were performed with no difference in the outcome (data not shown).
Ex vivo stromal cells were isolated as described above and non-adherent cells washed away after overnight culture (density comparable with lines); they were non-proliferative and therefore not irradiated.- BMDC: They were activated with 0.5 µg/ml LPS for 6 h at 37°C.
- 2 h after LPS addition 1 µM SIINFEKL peptide was added.
- 1×104 BM-DC were added per 24-well.
- T cells: They were obtained ex vivo from spleen and pLN dissected from CO2-killed WT B6 and OT-I transgenic mice and suspended by meshing.
- Erythrocytes were removed using red blood cell lysis buffer (Tris-Ammonium chloride based).
- CD8 cells were enriched by panning using antibodies to B220 (RA3-6B2), CD4 (H129.19.6), CD11b (M1/70) and CD11c (N418).
- OT-I cells were labeled…
Functional assays
-
Bone marrow was harvested from C57BL/6 mice and plated in a six-well dish at 1 × 106 cells/ml in 2 ml of lymphocyte media (RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FCS , 5 mM
l -Alanyl-l -Glutamine , 100 IU/ml penicillin–streptomycin and 2 mM β-mercaptoethanol with 5 ng/ml of Daedalus IL-7 or commercial IL-7 . - Media with IL-7 was replaced at Day 3 and the resulting cell populations were evaluated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) at Day 5.
- Cells were stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) anti-mouse IgM and PE anti-mouse B220 (BD) in FACS staining buffer (PBS with 2.5% FCS) and analyzed on an LSRII flow cytometer (BD) and using FlowJo software .
- Recombinant human LIF was tested for its ability to maintain pluripotency of murine ES cells.
- Briefly, murine ES cells (AB1 ES cells kindly provided by Steve Jones, University of Massachusetts) were plated on irradiated feeder cells with either…
Functional assays
-
Bone marrow was harvested from C57BL/6 mice and plated in a six-well dish at 1 × 106 cells/ml in 2 ml of lymphocyte media (RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FCS , 5 mM
l -Alanyl-l -Glutamine , 100 IU/ml penicillin–streptomycin and 2 mM β-mercaptoethanol with 5 ng/ml of Daedalus IL-7 or commercial IL-7 . - Media with IL-7 was replaced at Day 3 and the resulting cell populations were evaluated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) at Day 5.
- Cells were stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) anti-mouse IgM and PE anti-mouse B220 (BD) in FACS staining buffer (PBS with 2.5% FCS) and analyzed on an LSRII flow cytometer (BD) and using FlowJo software .
- Recombinant human LIF was tested for its ability to maintain pluripotency of murine ES cells.
- Briefly, murine ES cells (AB1 ES cells kindly provided by Steve Jones, University of Massachusetts) were plated on irradiated feeder cells with either…
Differentiation of CD34+ cells
- Erythroid differentiation was carried out on MS-5 stromal cells as previously described 4 cells were plated in 2 mL medium'>serum-free expansion medium containing 100 ng/ml SCF, 5 ng/ml IL-3, 3 U/ml erythropoietin (EPO), and 1 mM hydrocortisone and cultured in 6-wells plates at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 4 days.
- The cells were then diluted into 6 ml of the same medium in a 25 cm2 flask and cultured for an additional 4 days.
- Expanded cells were washed with basal medium and resuspended in 25 ml of basal medium with 3 U/ml EPO and plated onto a newly confluent 75 cm2 flask of MS-5 feeder cells and cultured for 3 days.
- For final maturation, erythroid cells were co-cultured on feeder cells for 10 days using basal medium without cytokines with one medium change after 5 days at which time 2×106
Functional assays
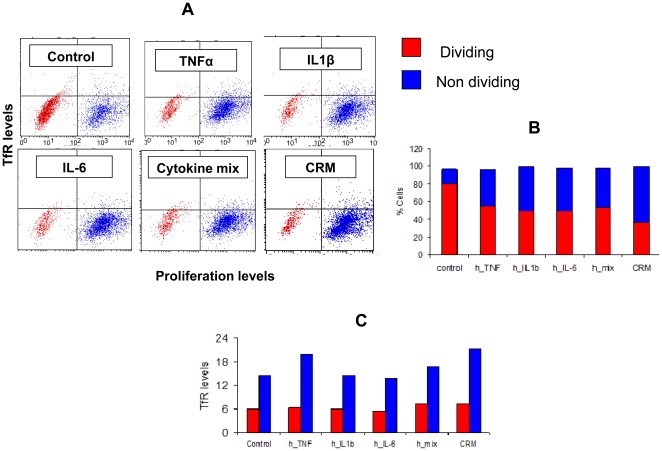
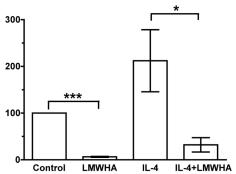
- For cytokine signalling, LN T cells (5 × 106 cells/ml) were cultured 16 h with recombinant mouse IL-7 (10 ng/ml), IL-4 (40 ng/ml), IL-6 (45 ng/ml& ) or IL-15 (100 ng/ml& ) as previously described (
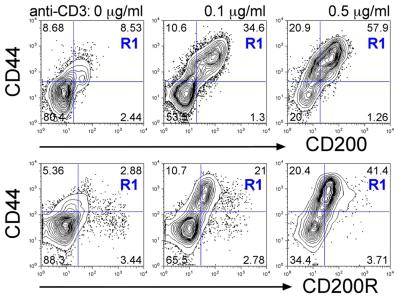
T cells co-express CD200 and CD200R following TCR activation.
- C. Naïve LN cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 (1 µg/ml) + anti-CD28 (2 µg/ml) either transiently on Ab-coated wells for the first 2d then removed to fresh media (blue lines) or chronically with Ab-coated aAPC present throughout the culture (red lines) in Th1 (top row), Th2 (middle row) or non-polarising (IL-7, bottom row) conditions.
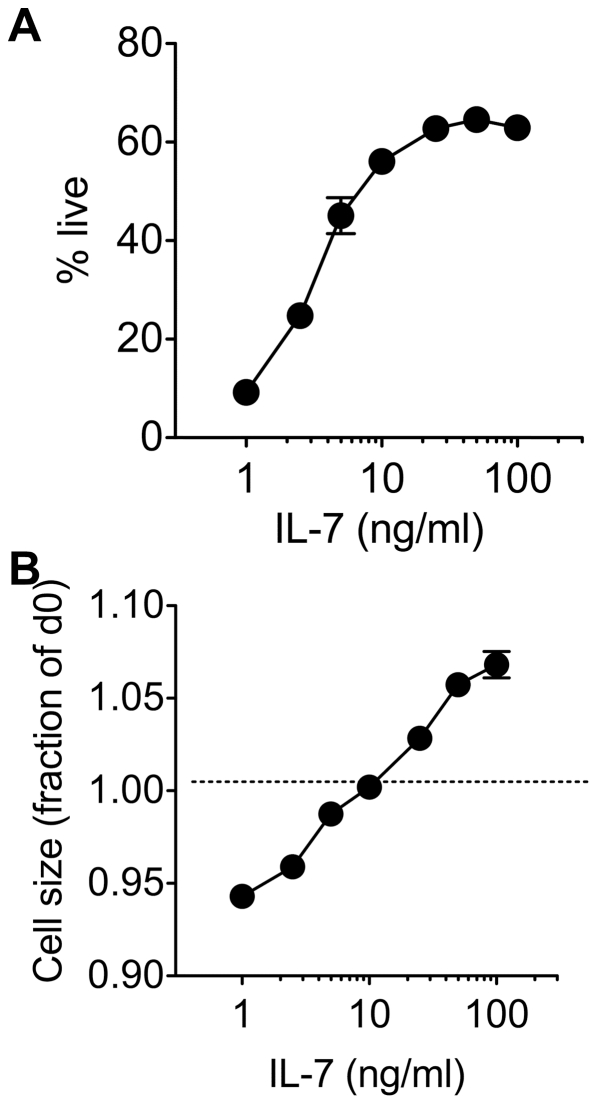
IL-7 mediated growth and survival is dose dependent in vitro.
- CD8 T cells were enriched from C57Bl6/J donors and cultured with a range of IL-7 concentrations.
Reduced white adipose tissue mass and insulin sensitivity in IL-7 overexpressing mice.
- Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of 7 WT mice (white bars) and 8 Tg IL-7 mice (black bars).
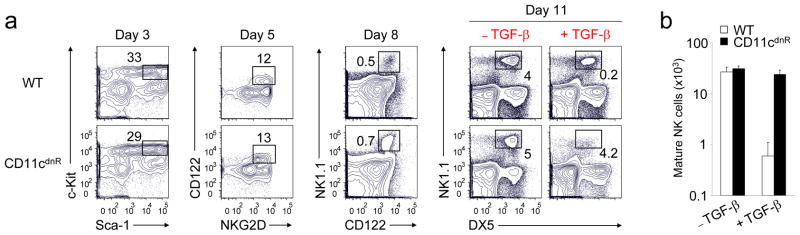
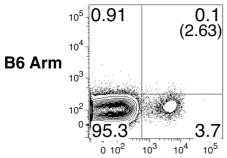
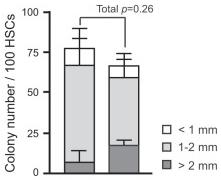
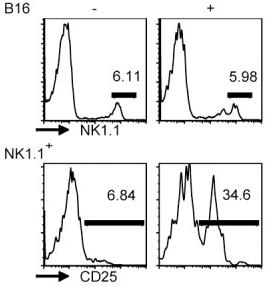
TGF-β is a negative regulator of NK cell generation CD11cdnR and wild-type mice were injected (i.p.)
- Four days later, mice were sacrificed and HSC-enriched bone marrow cells were cultured in the presence of IL-7, SCF, and Flt3L.
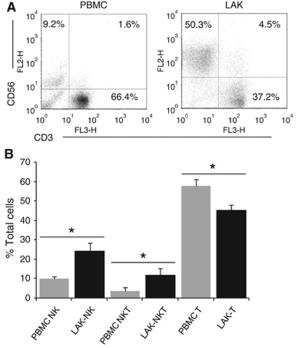
In vitro Generation of NK cells
-
The generation of NK cells from stem cell precursors was conducted
in vitro , based on protocol previously described. - Briefly, CD11cdnR and wild-type mice were first treated (
i.p. ) with 5-FU (5-Fluorouracil) provided at 150 mg/kg body weight. - Four days later, mice were sacrificed and HSC-enriched bone marrow cells were cultured at 10,000 cells/well in complete RPMI supplemented with 0.5 ng/ml murine IL-7 , 30 ng/ml mouse SCF , and 100 U/ml murine Flt3L (eBiosciences).
- Cells were re-fed with the same media on day 3.
- On day 5, cultures were harvested and re-plated at 15,000/well on a confluent monolayer of OP9 stromal cells in complete RPMI containing 30 ng/ml murine IL-15 .
- On day 8, cultures were re-fed with the same media with or without 5 ng/ml human TGF-β .
- On day 11, cells were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry.