Human VEGF 165AA Recombinant (E.Coli)
Categories: PDGF familyPDGF familyRecombinant Human Cytokines$70.00 – $3,500.00
Description
Accession
P15692
Source
Optimized DNA sequence encoding Human VEGF mature chain was expressed in Escherichia Coli
Molecular weight
Native human VEGF is generated by the proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and propeptide, the molecule has a calculated molecular mass of approximately 19kDa. Recombinant Vascular endothelial growth factor is a disulfide-linked homodimer protein consisting of 165 amino acid residue subunits, and migrates as an approximately 38 kDa protein under non-reducing and as 19 kDa under reducing conditions in SDS-PAGE.
Purity
>95%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
The ED(50) was determined by the dose-dependentproliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) using a concentration range of.0-10.0 ng/ml.
Protein Sequence
MNFLLSWVHW SLALLLYLHH AKWSQAAPMA EGGGQNHHEV VKFMDVYQRS YCHPIETLVD IFQEYPDEIE YIFKPSCVPL MRCGGCCNDE GLECVPTEES NITMQIMRIK PHQGQHIGEM SFLQHNKCEC RPKKDRARQE NPCGPCSERR KHLFVQDPQT CKCSCKNTDS RCKARQLELN ERTCRCDKPR R
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
RecombinantVEGF was lyophilized from.2 μm filteredmM PB solution, pH7.0 .
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at° -° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Interactor
Interactor
Interactor
Interactor
Interactor
Interactor
Interactor
Interactor
Biological Process
Biological Process
Molecular function
Molecular function
Molecular function
Methods
Endothelial Sprouting Assay
- Endothelial sprouting assay was performed as described 4 ESC were seeded in 35 mm dishes in 1.2 mg/ml collagen, type I neutralized with 0.1 N NaOH.
- Collagen media contained 15% FBS, 450 µm MTG, 10 µg/ml insulin , 50 ng/ml human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, , ), 100 ng/ml human basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2, , ) in IMDM.
- Cells were incubated at 37°C, 5% CO2.
- At day 6, 200 µl media without collagen was added and EB were analyzed on day 11.
- Image analysis was performed using AxioVision LE Software .
Endothelial differentiation and immunocytochemical analysis
- Endothelial differentiation was induced as described previously with some modifications [2) in each well.
- 1 × 104 hADSCs were seeded in plates and incubated for up to 15 days in medium'>medium'>medium'>endothelial medium'>medium'>differentiation medium'>medium containing medium'>medium'>medium'>endothelial medium'>growth medium'>medium (EGM2-MV) supplemented with 50 ng/mL vascular medium'>medium'>medium'>endothelial medium'>growth factor-165 (VEGF165) , 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin.
- 15 days after endothelial differentiation started, the cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature, and rinsed with PBS.
- The fixed cells were then incubated for 1 hour at 37°C with mouse antibodies against human CD31 or CD34 , KDR at 1:500 dilution.
- After incubation in a blocking solution containing 1% normal goat serum, they were…
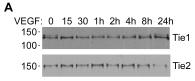
Effects of VEGF and TNFá on Tie1 and Tie2 Cleavage.
- HUVEC were incubated with VEGF A or TNFα B for times up to 24 h as indicated before cell lysis and detection of cellular full-length Tie1 by immunoblotting.
2.3. Differentiation of hESC
-
H1 hESCs were plated at 3 × 106 per well of 6-well ultralow attachment (ULA) plates in a total volume of 4 mL of medium'>X-VIVO-15 medium , supplemented with 1 mM sodium pyruvate, nonessential amino acids, 2 mM L-glutamine (all PAA Laboratories GmbH) and 5
μ M 2-mercaptoethanol . - The following growth factors were added: 50 ng/mL recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4, & ), 50 ng/mL recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor , 20 ng/mL recombinant human stem cell factor , and 50 ng/mL recombinant human granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF, & ).
- After 2-3 days, the medium was topped up with 2 mL of fresh supplemented X-VIVO-15 medium to produce a total volume of 6 mL.
- Subsequent feeding was performed every 2-3 days by replacing 2-3 mL of old medium with new supplemented X-VIVO-15 medium from which every 5 days a growth factor was removed starting with BMP-4 at day 5, followed by VEGF at…
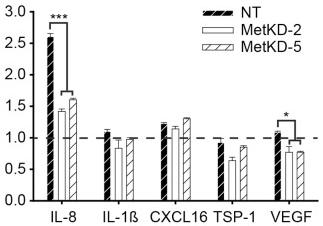
Met knockdown alters secretion of angiogenic factors.
- VEGF ELISA shows decreased VEGF levels in BxPC-3 and ASPC-1 MetKD xenografts relative to NT control tumors (***p<0.001; ANOVA).
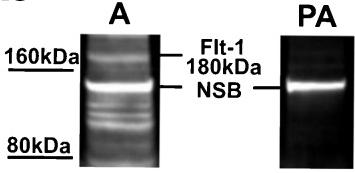
Specificity of the VEGF-A (a), Flt-1 (b) and KDR (c) antibodies in western blot analyses of ovine choroid plexus (CP) homogenates.
- d Representative blots of recombinant human (rh)VEGF-A121 (line 1), ovine CPs (lines 2 and 3) and rhVEGF-A165 (lines 4 and 5) resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with VEGF-A antibodies used in (a).
SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting
- The second part of CP was cut into small pieces, placed frozen into lysing Matrix D tubes with 500 μl of ice-cold lysis buffer consisting in 100 mM NaCl, 1 % Triton X-100, 2 mM EDTA, 0.2 % SDS, 0.5 % sodium deoxycholate and 1 % protease inhibitor cocktail and homogenized in the FastPrep instrument at an oscillation speed of 6.5 for 30 s. Disruption was repeated 3 times and between the cycles, samples were placed on ice.
- After the last cycle, tubes were briefly centrifuged at 5,000
g to remove any undisrupted tissues. - Homogenates were then transferred into new tubes and centrifuged at 13,000
g for 30 min at 4 °C. - The obtained supernatants were used for protein quantification using a Bradford kit (kit, , ).
- Aliquots of 100 μg of protein were stored at −20 °C until being loaded on SDS-polyacrylamide gradient gels (6–15 % for Flt-1 and KDR and 6–12 % for VEGF-A) and then transferred to a 0.45-μm PVDF membrane…
Generation and administration of UC-MSCs
- UCs (n = 10, clinically normal pregnancies, approved by the Qilu hospital’s human research ethics committee) were excised and washed in a 0.1 mol/l phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) to remove excess blood.
- The cords were dissected and the blood vessels were removed.
- The remaining tissues were cut into small pieces (1–2 mm3) and placed in plates with low-glucose medium'>ulbecco-modified medium'>Eagle medium (L-MEM) , supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 2 ng/mL vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF& , , ), 2 ng/mL epidermal growth factor (EGF& ), 2 ng/mL fibroblast growth factor (FGF& ), 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin .
- Cultures were maintained at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2.
- The media were changed every 3–4 d. Adherent cells proliferated from individual explanted tissues 7–12 d after initiating incubation.
- At this time, the small tissue pieces were removed from the culture and the adherent fibroblast-like…
Isolation of primary human LSECs
- Human liver endothelial cells were isolated from liver tissue from patients undergoing surgical liver resection.
- The tissue was collected with informed consent and under local ethics committee approval of the University of Bern.
- Approximately 30 g of liver was cut into 2 mm3 pieces and digested in 50 ml PBS containing 10 mg/ml collagenase 1A for 90 min at 37 °C.
- The resultant solution was then filtered through a sterile 0.5 mm steel mesh, the supernatant centrifuged at 300 ×
g for 8 min, and the pellet then resuspended on 10 ml PBS. - This digest was then layered on a 33%/77% Percoll density gradient, centrifuged for 30 min at 800 ×
g 4 °C and the non-parenchymal layer removed, pelleted and resuspended in 500μ l of PBS. - Endothelial cells were isolated from this fraction by immunomagnetic selection using a mouse anti-CD31 antibody , followed by an anti-mouse IgG Dynabead, 30 min incubation with each and magnetic separation was performed on MACS columns.
- Isolated LSECs were…