Human Macrophage Colony stimulating Factor Recombinant
Categories: PDGF familyPDGF familyRecombinant Human Cytokines$70.00 – $4,700.00
Description
Accession
P09603
Source
DNA sequence encoding the mature chain of Human CSF1 was expressed in E.coli.
Molecular weight
Recombinant Human CSF1 is a homodimer protein consisting of amino acid residues [33-191] migrates as an approximately 36 kDa protein on SDS-PAGE.
Purity
>95%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
The activity was determined by its ability to bind in functional ELISA assay.
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Recombinant CSF1 was lyophilized from 0.2 µm filtered PBS solution pH7.4
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers.
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least 2 years from date of receipt at -20° C.
Usage
This product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Interactor
Interactor
Interactor
P03228
Interactor
Interactor
P0CW72
Interactor
Q8UZD0
Biological Process
Biological Process
Molecular function
Molecular function
Methods
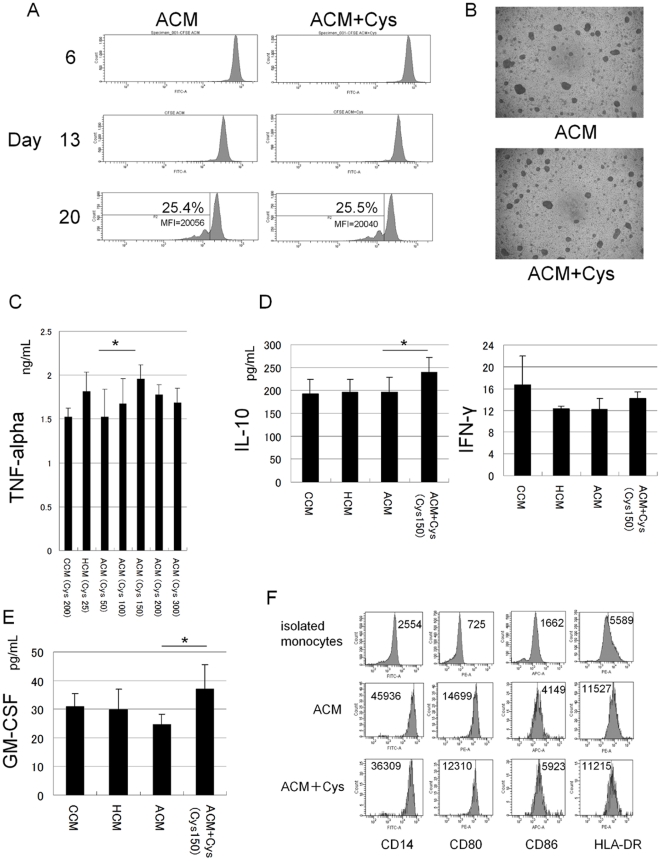
L-Cystine dose-dependently increased TNF-alpha from CD14+ monocytes with LPS under the amino acid environment of patients with advanced cirrhosis.
- A, Isolated CD14+ monocytes (purity >90%) were cultured at a density of 2.5×105 cells/well in 96-well plates containing in ACM and ACM plus L-Cys (L-Cys : 150 nmol/mL) with 1,000 U/mL M-CSF.
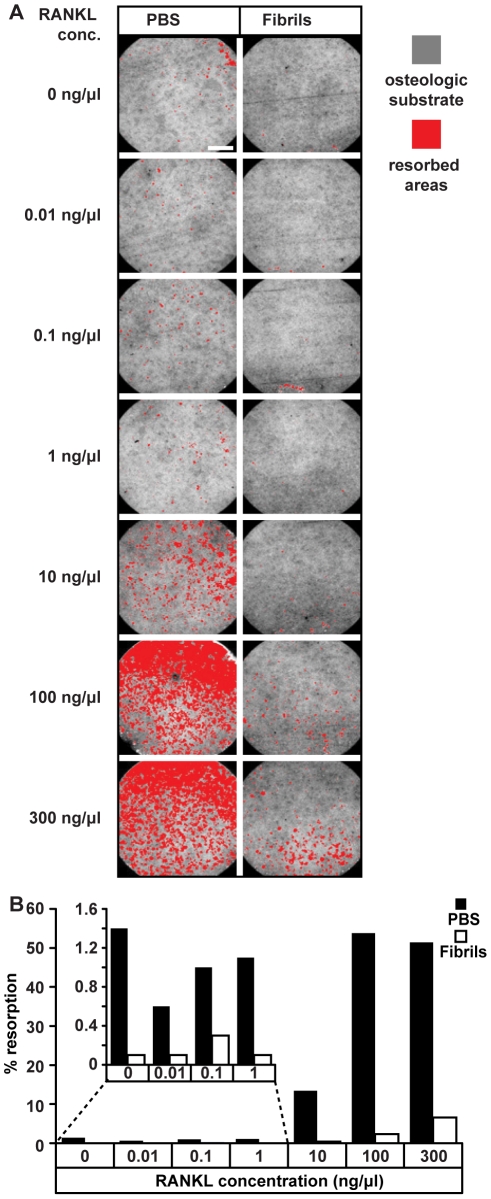
Effects of β2-microglobulin (β2m) fibrils on RANKL-dependent osteoclast formation.
- Primary human monocytes were incubated with M-CSF and the indicated concentrations of RANKL in the presence of PBS or 10 µg/ml β2m-fibrils for 14 days and their ability to resorb an osteologic substrate was then assessed.
Cell preparation
- Human peripheral blood was taken from the antecubital vein of healthy volunteers and collected into tubes containing sodium citrate (1% final concentration) to prevent coagulation.
- Leukocyte populations were then isolated by sedimentation with dextran (500,000 M.wt) followed by discontinuous Percoll™ gradient centrifugation, as reported previously +ve monocytes were cultured for 6 days in tissue culture plates in Iscove's Modified ulbecco's Medium (IMM; ) containing penicillin/streptomycin (PPA , 50 U/ml) and 10% heat-inactivated FCS , in the presence of 50 U/ml GM-CSF to generate Mph1, or 25 ng/ml M-CSF to generate Mph2.
- Following stimulation with LPS (E.coli, serotype O127∶B8) (10 ng/ml for 24 h) Mph1 cells secreted IL-12 but not IL-10, while Mph2 secreted IL-10 but little IL-12, confirming macrophage polarization
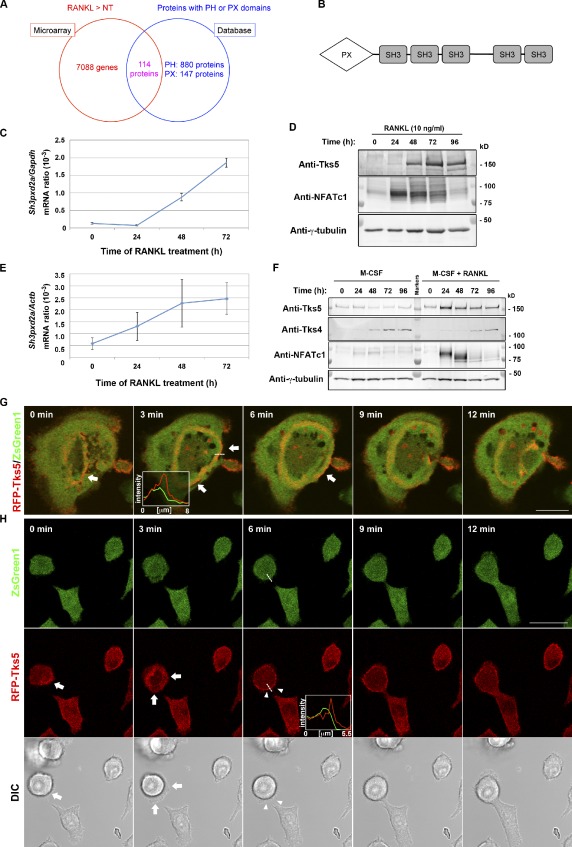
Tks5 as a potential mediator of fusion-competent protrusion formation.
- (E and F) Mouse bone marrow–derived macrophages cultured in the presence of 10 ng/ml M-CSF with or without 10 ng/ml RANKL for the indicated times were subjected either to quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the amount of Sh3pxd2a mRNA (normalized by that of Actb mRNA; E) or to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies .
Tks5 as a potential mediator of fusion-competent protrusion formation.
- (E and F) Mouse bone marrow–derived macrophages cultured in the presence of 10 ng/ml M-CSF with or without 10 ng/ml RANKL for the indicated times were subjected either to quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the amount of Sh3pxd2a mRNA (normalized by that of Actb mRNA; E) or to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies .
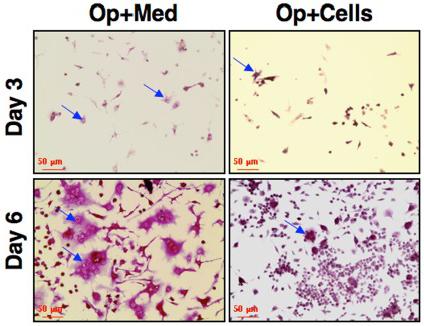
Impaired osteoclast differentiation, maturation and functionality in osteoporotic mice received CD34+ cells.
- Harvested bone marrow was subjected to differentiation towards osteoclasts using M-CSF and sRANKL (n = 5).
Human macrophage preparations
- Human macrophages were prepared as previously described 6 cells/ml, and seeded in six-well plates in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS .
- Macrophages were differentiated from monocytes in the presence of recombinant human M-CSF (50 ng/ml, , ) for 6 to 11 days.
- The purity of the cell preparations was evaluated by flow cytometry and over 85% of CD11b+/CD206+ macrophages were consistently obtained.
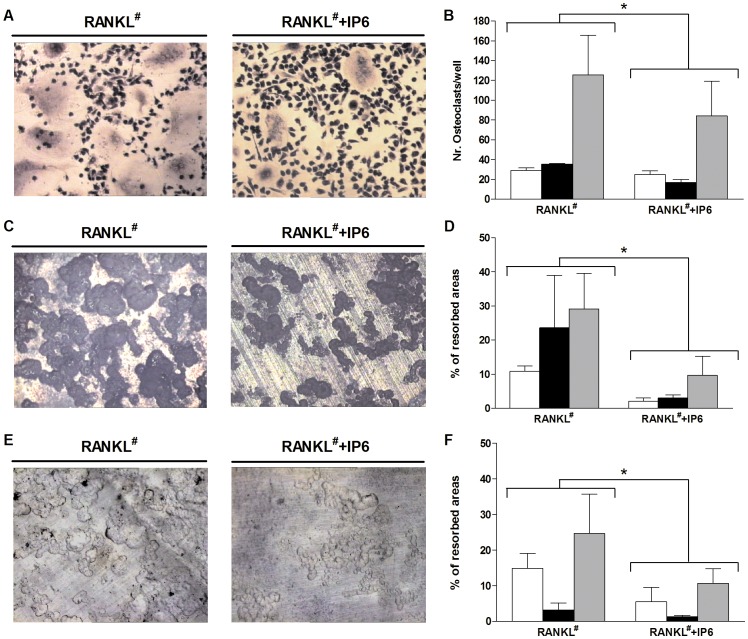
Effect of inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMNC) osteoclastogenesis and resorption activity on mature osteoclasts cells derived from human PBMNC.
- RANKL# refers to cells treated with RANKL and also with M-CSF and dexamethasone as described in the Materials & Methods section.
Effect of inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMNC) osteoclastogenesis and resorption activity on mature osteoclasts cells derived from human PBMNC.
- RANKL# refers to cells treated with RANKL and also with M-CSF and dexamethasone as described in the Materials & Methods section.