Human Interleukin-12 Recombinant
Categories: HematopoietinsRecombinant Human Cytokines$160.00 – $3,500.00
Description
Accession
P29460
Source
DNA sequence encoding Human Interleukin-12 mature chain was expressed in HEK cells.
Molecular weight
Native human Interleukin-12, generated by the proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and propeptide, the molecule has a calculated molecular mass of approximately 75 kDa. Recombinant Interleukin-12 is a disulfide-linked heterodimer protein consisting of 306 amino acid residue p40 subunit and a 197 amino acid residue p35 subunit, and migrates due to glycosylation as an approximately 50kDa and 40kDA protein under reducing conditions in SDS-PAGE.
Purity
>97%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
The ED(50) was determined by the dose-dependent proliferation ofactivated human T lymphoblasts. cells was found to be in the range of.1-0.2 ng/ml.
Protein Sequence
MCHQQLVISW FSLVFLASPL VAIWELKKDV YVVELDWYPD APGEMVVLTC DTPEEDGITW TLDQSSEVLG SGKTLTIQVK EFGDAGQYTC HKGGEVLSHS LLLLHKKEDG IWSTDILKDQ KEPKNKTFLR CEAKNYSGRF TCWWLTTIST DLTFSVKSSR GSSDPQGVTC GAATLSAERV RGDNKEYEYS VECQEDSACP AAEESLPIEV MVDAVHKLKY ENYTSSFFIR DIIKPDPPKN LQLKPLKNSR QVEVSWEYPD TWSTPHSYFS LTFCVQVQGK SKREKKDRVF TDKTSATVIC RKNASISVRA QDRYYSSSWS EWASVPCS RNLPVATP DPGMFPCLHH SQNLLRAVSN MLQKARQTLE FYPCTSEEID HEDITKDKTS TVEACLPLEL TKNESCLNSR ETSFITNGSC LASRKTSFMM ALCLSSIYED LKMYQVEFKT MNAKLLMDPK RQIFLDQNML AVIDELMQAL NFNSETVPQK SSLEEPDFYK TKIKLCILLH AFRIRAVTID RVMSYLNAS
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Recombinant Interleukin-12 was lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered PBS solution pH7.5.
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers.
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at2° -8° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Interactor
Interactor
Molecular function
Methods
Comparison of the gene expression patterns between donors and treatments.
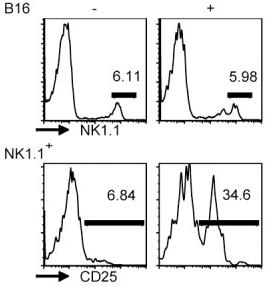
- The image depicts the log of the fold change of NK genes regulated due to co-culture with 3D7-infected erythrocytes (iRBCs) or with the cytokines IL-12 andIL-18.
NK92/iRBCs co-culture and flow cytometry
- NK92 cells were kept in two different environments for 24 hours prior to the co-culture: in normal cell medium'>medium medium'>(+rIL2; NK92 nm) and in cell medium'>medium without rIL-2 (starvation medium'>medium; NK92s).
- Cells from both environments were co-cultured with 3D7 schizont-infected erythrocytes and uRBCs (NK92-RBCs ratio: 1:3) in their respective growth medium.
- As a positive control, cells were also incubated with a mixture of IL-12 and IL-18 (and MBL, respectively; 100 ng/106 cells each).
- After the indicated time of incubation at 37°C and 5% CO2, NK cells from the co-culture as well as cells incubated without RBCs were stained for 30 min at 4°C with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies for surface CD56 (APC), CD3 (PE), CD16 (FITC), CD69 (FITC), CD25 (PE) in parallel with the appropriate isotype controls.
- Cells were also internally stained with the IFN-γ (PE) antibody (all…
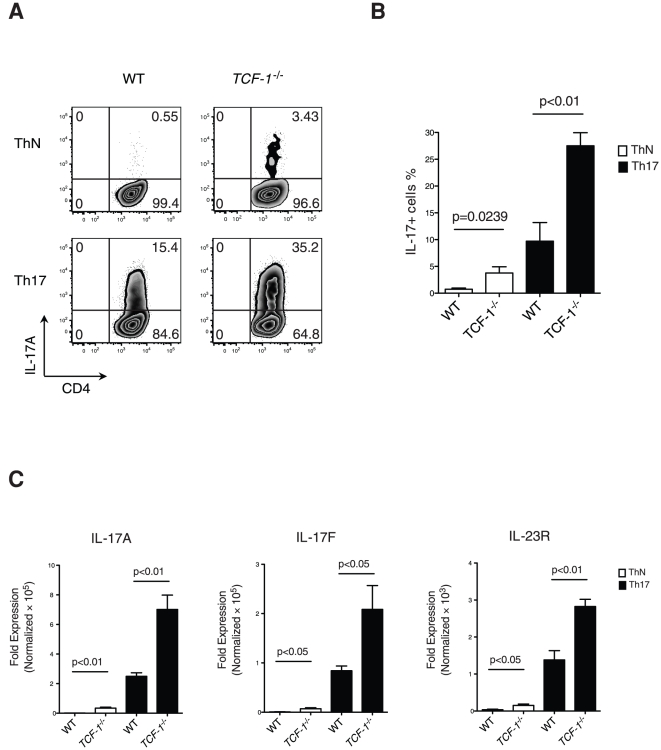
In vitro Induction of Allogeneic Th1 and Th2 cell Lines
- Purified human naïve CD4 T cells were stimulated with irradiated (100Gy) allogeneic Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) – transformed B cells (1∶1 ratio) in complete medium'>RPMI-8 medium at 105 cells/mL in round-bottom 96-well plate.
- Th1-biased cultures contained recombinant human IL-2 (5 ng/mL), recombinant human IL-12 (20 ng/mL) and anti-IL-4 (5 µg/ml& ).
- Th2-biased cultures contained recombinant human IL-2 (5 ng/mL), recombinant human IL-4 (20 ng/mL& ), anti-IL-12 (5 µg/ml, ebioscience) and anti-IFNγ (5 µg/ml& ).
- Fresh medium containing 5 ng/mL IL-2 was added if necessary to cultures showing strong proliferation.
- The cultures were restimulated and expanded every seven days.
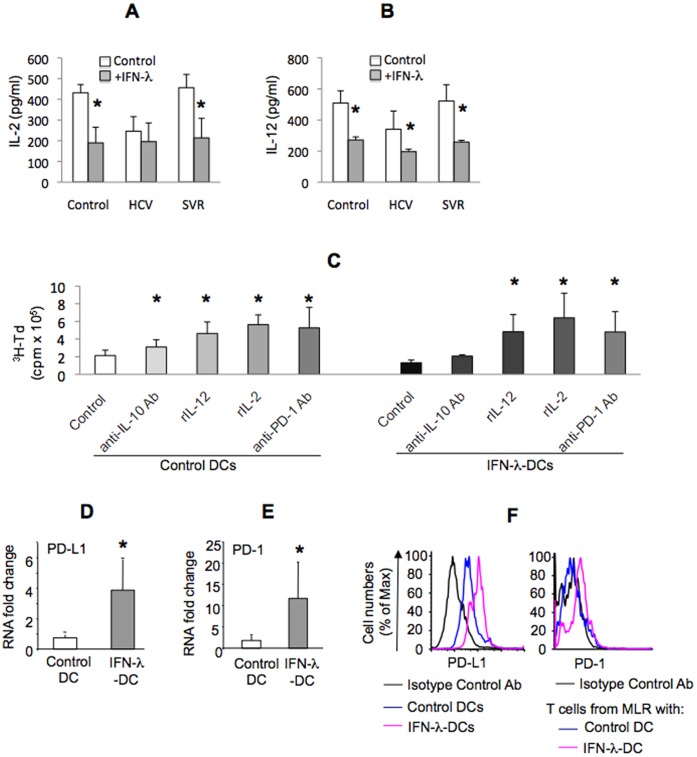
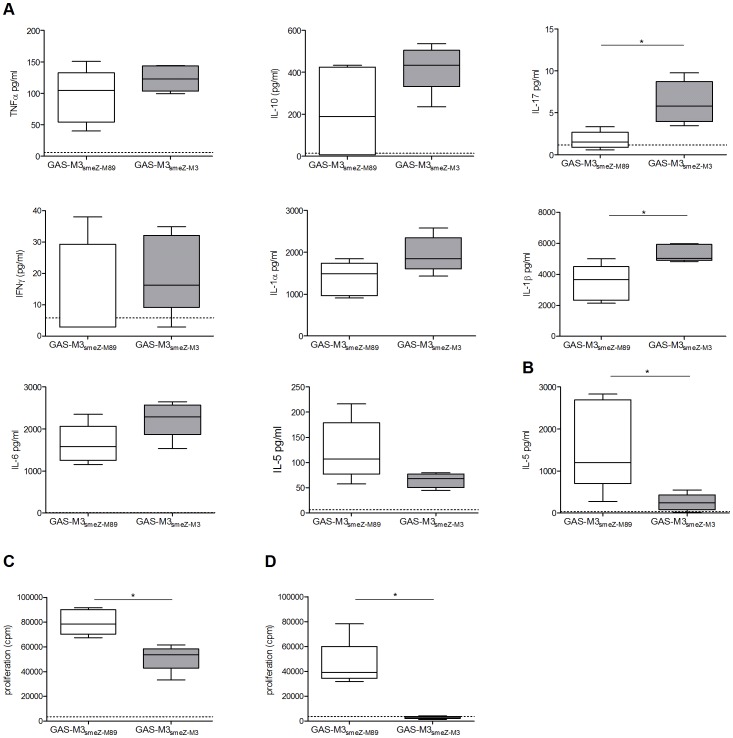
IFN-λ treatment-induced inhibitory DCs phenotype is dependent on IL-10 and PD-1/PD-L1 ligand.
- Co-culture supernatants from indicated groups were analyzed for IL-2 , IL-12 by ELISA; mean±SD pg/ml shown.
CTL Induction
- Naïve CD8+ T cells were negatively isolated from PBMCs of A24-positive donors using the CD8+ T cell isolation kit II and anti-CD45RO microbeads .
- The isolated cells were more than 95% pure CD45RO− CD8+ populations.
- These CD8+ T cells (1×106 cells/well) were cocultured with irradiated (100 Gy) aAPCs (1×105 cells/well) in 2 mL X-VIVO20 supplemented with 5% human AB serum (MP, , ) in wells of a 12-well plate in the presence of 10 ng/mL IL-12 .
- On day 3, 10 ng/mL IL-7 and IL-15 were added.
- Every 3 days, half the medium was exchanged for fresh medium containing 10 ng/mL IL-15.
- On day 12, the T cells were restimulated with γ-irradiated aAPCs.
- One day thereafter, IL-2 was added, to a final concentration of 20 U/mL.
- celltype'>To establish celltype'>T cell clones, a limiting dilution of the polyclonal Ccelltype'>TL was performed as…
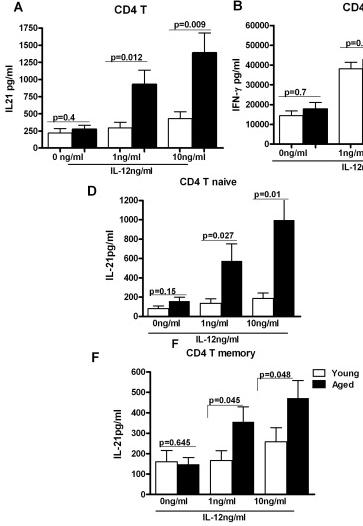
IL-21 secretion is increased from CD4+ T cells from aged subjects A, B, C Bar graph depicts the levels of IL-21 (A), IFN-γ (B), IL-17 (C) in the supernatant from aged and young total CD4+ T cells after stimulation with IL-12 for 5 days.
- D, F. Bar graph depicts the levels of IL-21 secreted from aged and young, Naïve CD4+ T cells and memory CD4+ T cells after stimulation with IL-12 for 5 days.
Vaccination and tumour challenge
- At 6 weeks HIS mice were distributed into two groups with matched levels of CD45+ human circulating cells.
- A group was subjected to two cycles of anti-HER-2 cell vaccination according to a schedule previously reported highly effective in HER-2/neu transgenic models (6 mitomycin-treated cells (to block proliferation) in 0.4 ml PBS.
- In the third week mice received five times daily administration of recombinant human IL-12 in 0.2 ml PBS supplemented with 0.01% mouse serum albumin .
- The dose of IL-12 was 50 ng per mouse per day in the first 4-week cycle and 100 ng per mouse per day in all subsequent cycles.
- The fourth-week mice received no treatment.
- The 4-week vaccination cycle was repeated twice.
- Non-vaccinated group received the injection of PBS or PBS supplemented with mouse serum albumin.
Blood samples, cells and cell cultures
- Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were prepared on a Ficoll-Paque density gradient by centrifugation (800 g, 30 min at room temperature), washed twice and frozen in RPMI 1640-FCS (5%)-DMSO (8.7%)-methyl-cellulose (0.1%).
- NK cells were selected from PBMCs by magnetic cell sorting using indirect NK isolation kit according to manufacturer's recommendations.
- Average celltype'>NK cell purity checked by flow cytometry (CD3−/CD16+/−/CD56+/−) was 97.51% ± 2.47 (standard deviation) across all donors.
- NK cells were cultured in complete RPMI 1640 medium, including 1 mM sodium pyruvate, and 1% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum.
- Recombinant human IL-2 and IL-12 were obtained from .
Establishment of antigen specific T-cell cultures and clones
- Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) isolated from a melanoma patient were stimulated with irradiated (25 Gy) autologous IκB10-loaded DCs (PBL:DC ratio = 3 × 106:3 × 105).
- The following day IL-7 (5 ng/mL) and IL-12 (10 ng/mL) were added.
- Stimulation of the cultures were performed every 8 d with IκB10-loaded irradiated autologous DCs (2×) followed by IκB10-loaded irradiated autologous PBLs (3×).
- After each stimulation, 120 U/mL IL-2 was added.
- The established cultures were tested for specificity for IκB10 after 4th stimulation.