Human Hepatocyte Growth Factor Recombinant
Categories: PDGF familyPDGF familyRecombinant Human Cytokines$70.00 – $4,300.00
Description
Accession
P14210
Source
Optimized DNA sequence encoding Human Hepatocyte Growth Factor mature chain was expressed in Chinese Hamster Ovary cell line.
Molecular weight
Native human Hepatocyte Growth Factor is generated by the proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and propeptide, the molecule has a calculated molecular mass of approximately kDa. Recombinant HGF is a glycosylated disulfide-linked heterodimeric protein consisting of alpha chain (463)and the beta chain (234)amino acid residue subunits, and migrates as an approximately 80 kDa protein under non reducing conditions in SDS-PAGE.
Purity
>97%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
The ED(50) was determined by the dose-dependent stimulation of the proliferation ofmurine BNL-CL2cell li was found to be in the range of.0-40.0 ng/ml.
Protein Sequence
MWVTKLLPAL LLQHVLLHLL LLPIAIPYAE GQRKRRNTIH EFKKSAKTTL IKIDPALKIK TKKVNTADQC ANRCTRNKGL PFTCKAFVFD KARKQCLWFP FNSMSSGVKK EFGHEFDLYE NKDYIRNCII GKGRSYKGTV SITKSGIKCQ PWSSMIPHEH SFLPSSYRGK DLQENYCRNP RGEEGGPWCF TSNPEVRYEV CDIPQCSEVE CMTCNGESYR GLMDHTESGK ICQRWDHQTP HRHKFLPERY PDKGFDDNYC RNPDGQPRPW CYTLDPHTRW EYCAIKTCAD NTMNDTDVPL ETTECIQGQG EGYRGTVNTI WNGIPCQRWD SQYPHEHDMT PENFKCKDLR ENYCRNPDGS ESPWCFTTDP NIRVGYCSQI PNCDMSHGQD CYRGNGKNYM GNLSQTRSGL TCSMWDKNME DLHRHIFWEP DASKLNENYC RNPDDDAHGP WCYTGNPLIP WDYCPISRCE GDTTPTIVNL DHPVISCAKT KQLRVVNGIP TRTNIGWMVS LRYRNKHICG GSLIKESWVL TARQCFPSRD LKDYEAWLGI HDVHGRGDEK CKQVLNVSQL VYGPEGSDLV LMKLARPAVL DDFVSTIDLP NYGCTIPEKT SCSVYGWGYT GLINYDGLLR VAHLYIMGNE KCSQHHRGKV TLNESEICAG AEKIGSGPCE GDYGGPLVCE QHKMRMVLGV IVPGRGCAIP NRPGIFVRVA YYAKWIHKII LTYKVPQS
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Interleukin-6 was lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in.5% glycine,.5% sucrose,.01% Tween80, mM Glutamic acid, pH.5.
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at2° -8° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Interactor
Interactor
Interactor
Molecular function
Molecular function
Methods
Silencing of mda-9/syntenin in 92.1 uveal melanoma cells inhibits in vitro invasion and HGF mediated signaling.
- B: Invasion of matrigel membranes by 92.1 cells towards different stimuli: medium with 10% serum , 50% conditioned medium from MG63 cell line , 100 ng/ml recombinant HGF in 0.1% serum.
Hepatogenic differentiation
- Cells were seeded at a concentration of 5000 cells/cm2 on tissue culture plastic plates and coverslips coated with Matrigel and cultured in high glucose DMEM supplemented with 1% penicillin/streptomycin , 2 mM L-Glutamine and 10% FBS for 3 days.
- The media were then changed to high glucose DMEM supplemented with 15% FBS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin, 2 mM L-glutamine, 300 µM monothioglycerol , 20 ng/ml hepatocyte growth factor , 10 ng/ml oncostatin M , 10−7 dexamethasone , 100 ng/ml FGF4 and 1X ITS (insulin, transferrin, selenium).
- The cells were allowed to differentiate for 21 days and then fixed and stored in PBS for immunofluorescence.
- The differentiation media were collected and analysed for the presence of urea secreted by the differentiated cells.
- Urea was subsequently measured using the urea/ammonia determination kit (R-Biopharm AG, Darmstadt, Germany) according to the manufacturers instructions, with positive control being urea (as per manufacturer's instructions) and…
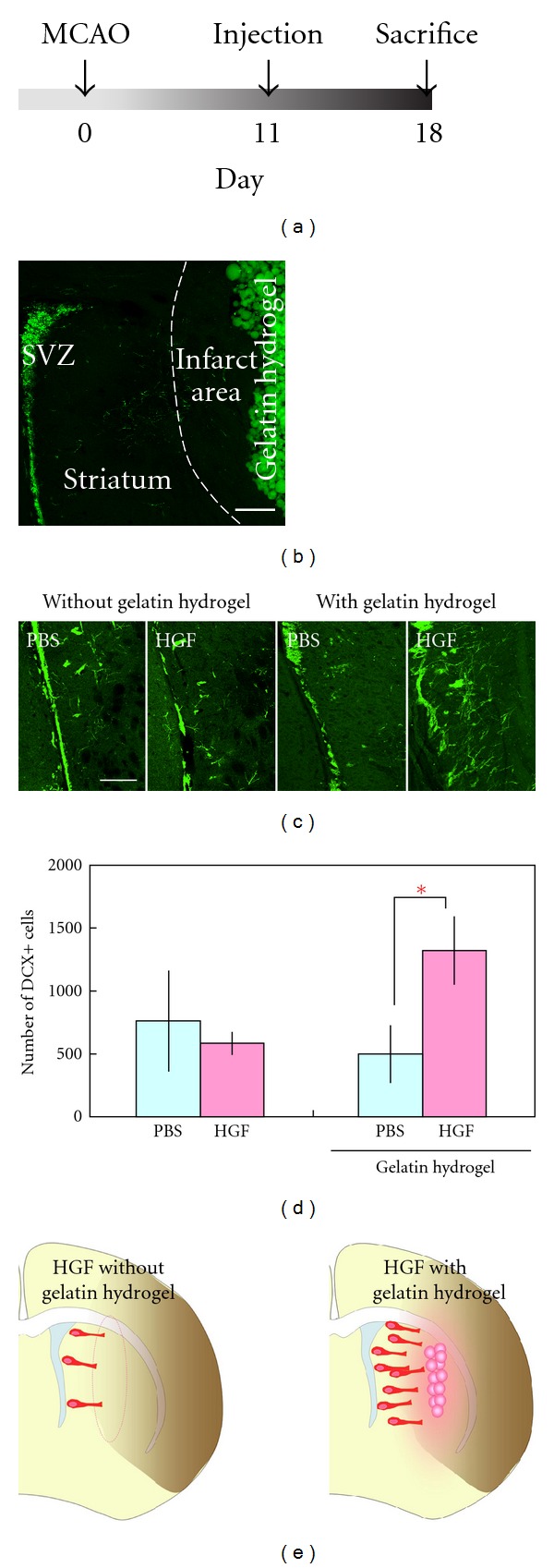
Effects of HGF-containing gelatin hydrogel on the number of new neurons migrating in the ischemic striatum after middle cerebral artery occlusion.
- (c) Coronal sections stained for DCX (green) from brains that received a PBS or HGF injection with (n = 6 animals for each group) or without (n = 4 animals for each group) gelatin hydrogel.
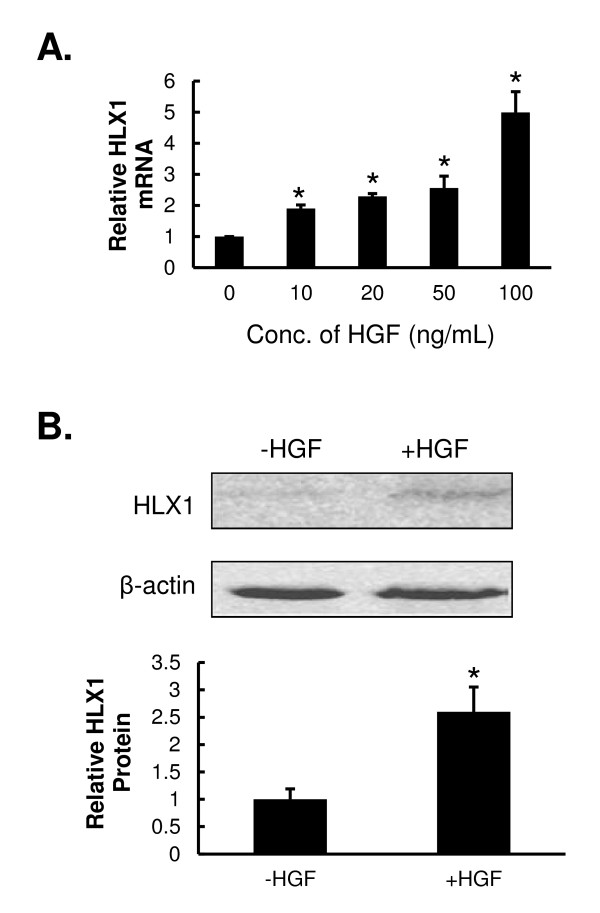
HGF up-regulates the expression of HLX1 in HTR-8/SVneo cells.
- HTR-8/SVneo cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of HGF for 48 h. The steady-state mRNA level of HLX1 was examined by qPCR and normalized to a β-actin internal control.
Isolation of primary human LSECs
- Human liver endothelial cells were isolated from liver tissue from patients undergoing surgical liver resection.
- The tissue was collected with informed consent and under local ethics committee approval of the University of Bern.
- Approximately 30 g of liver was cut into 2 mm3 pieces and digested in 50 ml PBS containing 10 mg/ml collagenase 1A for 90 min at 37 °C.
- The resultant solution was then filtered through a sterile 0.5 mm steel mesh, the supernatant centrifuged at 300 ×
g for 8 min, and the pellet then resuspended on 10 ml PBS. - This digest was then layered on a 33%/77% Percoll density gradient, centrifuged for 30 min at 800 ×
g 4 °C and the non-parenchymal layer removed, pelleted and resuspended in 500μ l of PBS. - Endothelial cells were isolated from this fraction by immunomagnetic selection using a mouse anti-CD31 antibody , followed by an anti-mouse IgG Dynabead, 30 min incubation with each and magnetic separation was performed on MACS columns.
- Isolated LSECs were…
Migration assays
- For the migration assay, the lower chamber contained DMEM, DMEM with 10% FBS with or without hEGF or hHGF (1039), primary cultured astrocytes, glioma C6 cells, or CM derived from ReNcells CX, astrocytes or glioma C6 cells.
- In some experiments recombinant human soluble CTAM (, & , , 1695-C) was added at a concentration of 20 µg/ml to the apical compartment of .
Migration Assays
- Assays were performed either with young NHEKs or PSE-NHEKs.
- Cells were starved in basal keratinocyte medium (KBM) for 16 h and then seeded in KBM onto Transwell® cell culture inserts with 8-µm pore size at a density of 30,000 cells per well (24-well format).
- Different attractant media were placed in the lower chambers: 100% KBM (control) or 90% KBM-10% FGM, 90% KBM-10% YF-CM, 90% KBM-10% SF-CM, or 90% KBM-10%, CM harvested from NHDFs treated with 12.5 µM GM6001 or transfected with siRNA (see the specific paragraph for the protocol of siRNA transfection).
- Alternatively, activated recombinant MMP-1 or MMP-2 , dissolved at 50 µM in FGM, or recombinant HGF-SF or recombinant TGF-β1 , dissolved at 10 ng/ml in KBM, was used as attractant.
- As recombinant MMP-1 and MMP-2 are provided as inactive pro-forms, they were activated prior to use in migration assays by incubation for 2 h at 37°C…
In vitro differentiation
- The following inductive differentiation systems were used: 1) For neural induction, E-PZ-iPS-like cells cultured on Matrigel were digested with collagenase type IV and seeded at a density of 1.0×105 cells/cm2 on a poly-HEMA-coated dish .
- After culture for 7 d in medium'>Neurobasal medium supplemented with 1× B-27 , 30 ng/mL bFGF and 30 ng/mL epidermal growth factor to induce sphere formation, spheres were then transferred onto poly-L-lysine-coated dishes and cultured for 10 d in α-MEM supplemented with 2% FBS, 25 ng/mL bFGF, and 25 ng/mLNF ; 2) Adipocyte and osteocyte inductions were performed according to the Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit ; 3) For hepatocyte induction, cells at a density of 2.0×104 cells/cm2 were cultured on collagen-coated dishes for 14 d in MEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 1× insulin-transferrin-selenium , 10 nM dexamethasone , 100…
In vitro differentiation
- The following inductive differentiation systems were used: 1) For neural induction, E-PZ-iPS-like cells cultured on Matrigel were digested with collagenase type IV and seeded at a density of 1.0×105 cells/cm2 on a poly-HEMA-coated dish .
- After culture for 7 d in medium'>Neurobasal medium supplemented with 1× B-27 , 30 ng/mL bFGF and 30 ng/mL epidermal growth factor to induce sphere formation, spheres were then transferred onto poly-L-lysine-coated dishes and cultured for 10 d in α-MEM supplemented with 2% FBS, 25 ng/mL bFGF, and 25 ng/mLNF ; 2) Adipocyte and osteocyte inductions were performed according to the Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Functional Identification Kit ; 3) For hepatocyte induction, cells at a density of 2.0×104 cells/cm2 were cultured on collagen-coated dishes for 14 d in MEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 1× insulin-transferrin-selenium , 10 nM dexamethasone , 100…
2.2. Induction of Hepatogenic Differentiation In Vitro
-
The WJMSCs-SUT1 and WJMSCs-SUT2 were expanded until reaching 90% confluence and then subjected into hepatocytes differentiation processes by using our new two-step protocol (
μ g/mL streptomycin , 2μ g/mL amphotericin B (Bristol-Myers Squibb, , ), 20 ng/mL human hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) , 10 ng/mL fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF-4) , and 5 mM nicotinamide for 7 days. - Subsequently, these cells were further cultured in stage 2 differentiation medium to achieve hepatic maturation which had components as serum-free DMEM-LG supplemented with 100 U/mL penicillin ; 100
μ g/mL streptomycin ; 2μ g/mL amphotericin B (Bristol-Myers Squibb, , ); 40 ng/mL oncostatin M (OSM) ; 2μ M dexamethasone , and 20μ l/mL insulin, transferrin, and selenium (ITS + premix) for up to 18 days. - The differentiation medium was changed twice a week.
- The undifferentiated cells from both 2 cell lines were included as negative controls.