Description
Accession
Q64314
Source
Optimized DNA sequence encoding extracellular domain of mouse CD34 including a C-terminal 6His tag was expressed in HEK293 cells.
Molecular weight
Recombinant mouse CD34 is a monomer protein consisting of 270 amino acid residue subunits, due to glycosylation migrates as an approximately 50 kDa protein on SDS-PAGE.
Purity
>95%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
Measured by the ability to support the adhesion of the HUVEC cell line. Coated plates with immobilized recombinant mouse CD34 ( 0.8 μg/mL) are able to adhere 40% of cells ( 4 x 104 cells/well) after one hour at 37 ℃
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Recombinant mouse CD34 is supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered PBS solution, pH7.2.
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least 2 years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at 2° - 8° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Biological Process
Methods
ELISA
- The concentrations of TNFα, CXCL12 and CCL2 were measured in cell supernatants by using ELISA kits in accordance with the manufacturer's protocols (TNFα and CXCL12 from R&D systems; CCL2 from) on an ETIMax-3000 reader .
- Supernatants were collected 24 h after infection, spun at 10,000 rpm for 10 min to discard bacteria and cell debris, and stored at −80°C until assayed.
Organoid cultures
- Primary crypts were cultured according to Sato et al. using reduced concentrations of murine recombinant-spondin1 (500ng/mL –& ) and varying concentrations of EGF .
- Organoid structures were imaged at day 6.
- Cell proliferation was measured by BrdU incorporation by incubation with 20μM BrdU for 1 hour at 37°C before fixation.
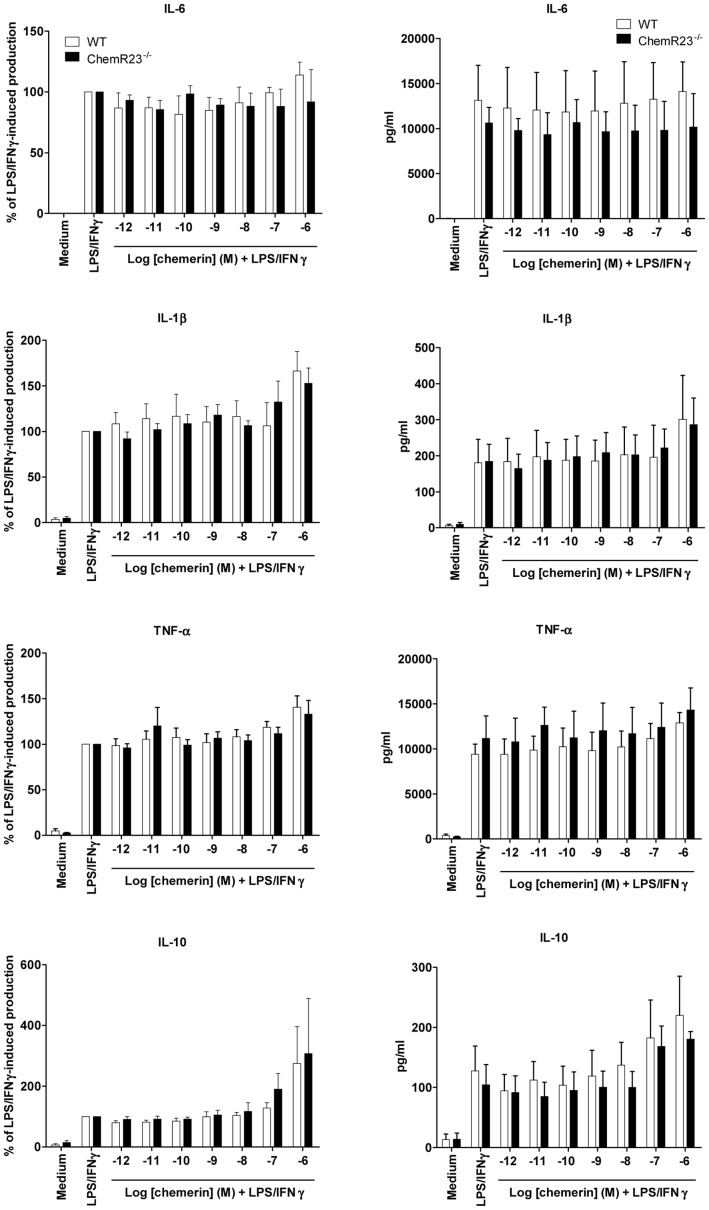
Dose-response effects of chemerin on the production of cytokines by activated peritoneal macrophages.
- Bio-Gel injection and selected by adherence, were tested for their production of pro-inflammatory (IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokines in response to stimulation by LPS and IFN-γ, in the presence or not of graded concentrations of recombinant chemerin (from 10−12 to 10−6 M).
Crypt culture media
- Isolated crypts were counted and embeded in matrigel ( 356231 growth factor reduced) that contains 1 μM Jagged (Ana-Spec) at 5–10 crypts/μl and cultured in a modified form of medium as described in.
- Briefly, MEM/F12 was supplemented by EGF 40 ng/ml , Noggin 200 ng/ml -spondin 500 ng/ml (&or ), N-Acetyl-L-cysteine 1 μM and Y-27632 dihydrochloride monohydrate 20 ng/ml .
- cADPR , when indicated, was added to culture at 50 μM.
- 30–50 μl drops of matrigel with crypts were plated onto a flat bottom 48-well plate ( 3548) and allowed to solidify for 20 to 30 minutes in a 37° C .
- 350 μl of crypt culture medium was then overlaid onto the matrigel, changed every other day, and maintained at 37°C in fully humidified chambers containing 6% CO2.
- Clonogenicity (colony-forming efficiency) was calculated by plating 50 to 400 crypts and assessing organoid formation 3 to 7 days after initiation…
-
Hepatic. Cells were seeded at a concentration of 5,000 cells/cm2 on tissue culture plastic plates and coverslips coated with Matrigel and cultured in high glucose DMEM supplemented with 1% Penicillin/Streptomycin , 2 mmol/lL -Glutamine and 10% FBS for 3 days. - The media were then changed to high glucose DMEM supplemented with 15% FBS, 1% Penicillin/Streptomycin, 2 mmol/l
L -Glutamine, 300 µmol/l Monothioglycerol , 20 ng/ml Hepatocyte Growth Factor , 10 ng/ml Oncostatin M , 10−7 Dexamethasone , 100 ng/ml FGF4 , and 1X ITS . - The cells were allowed to differentiate for 21 days and then fixed and stored in PBS for immunofluorescence.
- The differentiation media were collected and analyzed for the presence of urea secreted by the differentiated cells.
- Urea was subsequently measured using the Urea/Ammonia determination kit (R-Biopharm AG, Darmstadt, Germany) according to the manufacturers' instructions.
- Cells were subsquently assessed for expression of the hepatocyte markers ALBUMIN and…
Chemotaxis assay
-
The directional movement of cells toward the HGF gradient was evaluated using modified Boyden's chamber with 8-
μ m pore polycarbonate membrane inserts . - The cells detached with 0.25% trypsin were seeded into the upper chamber of an insert at a density of 2.5 × 104 in 100
μ l. - The lower chamber was filled with a prewarmed medium containing hHGF (20 ng/ml), mouse HGF (50, 100, 200 ng/ml) both from& , , , or SF-1 (100 ng/ml) .
- 0.5% BSA medium'>DMEM medium was used as a negative control.
- Inserts were removed from the transwell after 24 h and the cells were fixed with methanol.
- The cells that did not migrate were scraped off with cotton wool from the upper membrane and cells that had transmigrated to the lower side of the membrane were stained with Wright solution and counted under high power field with inverted microscope (Olympus IX70, Olympus Optical Co., , , ).
- Five fields were counted…
Chemotaxis assay
-
The directional movement of cells toward the HGF gradient was evaluated using modified Boyden's chamber with 8-
μ m pore polycarbonate membrane inserts . - The cells detached with 0.25% trypsin were seeded into the upper chamber of an insert at a density of 2.5 × 104 in 100
μ l. - The lower chamber was filled with a prewarmed medium containing hHGF (20 ng/ml), mouse HGF (50, 100, 200 ng/ml) both from& , , , or SF-1 (100 ng/ml) .
- 0.5% BSA medium'>DMEM medium was used as a negative control.
- Inserts were removed from the transwell after 24 h and the cells were fixed with methanol.
- The cells that did not migrate were scraped off with cotton wool from the upper membrane and cells that had transmigrated to the lower side of the membrane were stained with Wright solution and counted under high power field with inverted microscope (Olympus IX70, Olympus Optical Co., , , ).
- Five fields were counted…
Cell culture and hepatic cell differentiation
- Huh7 and Huh7.5 cells were provided by Jane C. Moores (The Reagent of the University of California, Oakland, CA).
- The cells were maintained in medium'>Dulbecco's medium'>modified medium'>Eagle's medium (DMEM;, , ) containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2.
- For hepatic differentiation, passages 3–7 of AT-hMSCs were plated at 1×104 cells/cm2 and incubated overnight.
- The cells were then washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and incubated in basal medium [60% DMEM-low glucose , 40% MCDB201 , and 1% penicillin/streptomycin] with 20 ng/ml EGF and 10 ng/ml bFGF for 2 days.
- After incubation, hepatogenic cytokines and growth factors were sequentially added as follows: days 0–7 (step 1), basal medium with 20 ng/ml HGF and 10 ng/ml bFGF; and days 7–21 (step 2), basal medium containing 20 ng/ml oncostatin M , 1 µmol/L dexamethasone…
Crypt isolation and culture
-
Colonic crypts were isolated from the distal colon of C57BL6 or LGR5EGFP mice, as previously described (
d -glucose 5.5 mM, Na2HPO4 1 mM, MgCl2 0.5 mM, CaCl2 1 mM; and placed in HEPES-buffered saline that was devoid of both Ca2+ and Mg2+, and supplemented with EDTA (1 mM), for 1 h at room temperature. - Crypts were liberated by serial rounds of vigorous shaking, crypt sedimentation, and collection.
- A total of 50–100 crypts was embedded in a 200-μl droplet of Matrigel Matrix, Growth Factor Reduced (VWR) and seeded on No. 0 coverslips (VWR International) contained within a 12-well plate .
- After polymerization at 37°C for 5–10 min, crypts were flooded with 0.5 ml mouse colonic crypt culture medium (advanced F12/MEM containing B27, N2,
n -acetylcysteine [1 mM], HEPES [10 mM], penicillin/streptomycin [100 U/ml], GlutaMAX [2 mM], epidermal growth factor [50 ng/ml], Wnt-3A [100 ng/ml][100 ng/ml] [all from] and-spondin 1 [1 μg/ml& ]). - For the human…
In vitro crypt culture
- Crypt isolation was carried out as previously described−1 murine epidermal growth factor, 100 ng μl−1 murine Noggin , 500 ng μl−1 mouse recombinant-Spondin 1 was added to each well.
- The number of crypts seeded per well was then quantified.
- The plate was then transferred to a where 10 crypts were randomly chosen to be monitored every 6 h for 10 days to obtain growth curves.
- Crypt culture medium was changed every 2 days and total organoid growth frequency was quantified after 10 days.