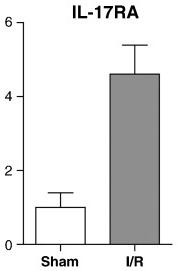
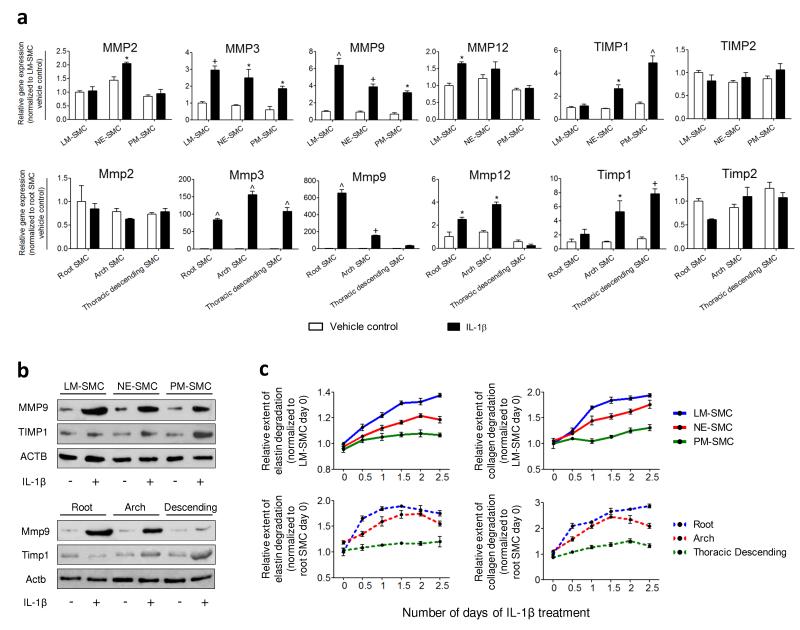
Rat Epidermal Growth Factor Recombinant
Category: Recombinant Rat Cytokines$70.00 – $900.00
Description
Accession
P07522
Source
Optimized DNA sequence encodingrat EGF mature chain was expressed in Escherichia Coli.
Molecular weight
RecombinantRat EGF, generated by the proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and propeptide, is a monomer protein. Recombinant Rat EGF consists of 54 amino acidsandmigrates as an approximately6.2 kDa protein under reducing conditions.
Purity
>97%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
The ED50 was determined by a cell proliferation assay using balb/c 3T3 cells is ≤ 0.1 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of ≥ 1 x 107 units/mg.
Protein Sequence
970 980 990 1000 1010 1020 STAPSLLGED GHHLDRNSNT GCPPSYDGYC LNGGVCMYVE SVDRYVCNCV IGYIGERCQH 1030 1040 1050 1060 1070 1080 RDLRWWKLR H AGYGQKHDIM VVAVCMVALV LLLLLGMWGT YYYRTRKQLS NPPKNPCDEP
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Rat EGF was lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS pH 7.5.
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least 2 years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at 2° - 8° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Molecular function
Methods
Rat CDC isolation and culture
-
Rat CDCs were cultured according to the method of Smith
et al 2 at 37°C, small, round, phase bright cells grew out from the explants over a bed of stromal-like cells. - Once they reached 80–90% confluency, these explant-derived cells (EDCs) were isolated using trypsin and re-plated on poly-d-lysine coated 24 well plates in cardiosphere growth medium'>medium medium'>(CGM) comprising 65% medium'>Dulbecco's medium'>modified medium'>eagle medium'>medium (DMEM/F12), 35% IMDM, 7% FBS, 2% B27 , 25 ng/ml cardiotrophin , 10 ng/ml epidermal growth factor (EGF ), 20 ng/ml basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and 5 units thrombin .
- EDCs could be harvested every 7 days, for up to 4 weeks.
Time-lapse imaging assay
- Cells were transfected with fucci2;mAG-hGem(1/110), which labels nuclei in the S/G2/M phases 2/M marker were grown in 96-well dishes in serum-free DMEM HAM/F12 supplemented with 1×B27 , 20 ng/mL epidermal growth factor (EGF), and 20 ng/mL fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), at 37°C with 5% CO2.
- The cells were imaged for 96 hours in an incubator on the microscope stage.
- Fifty-one images in the z-axis, both bright-field and single-color (green), were captured at 20-min intervals.
- An inverted microscope (IX-71, Olympus) was fitted with a Nipkow disc scanning confocal unit (CSU10, Yokogawa Electric Corp.), EM-CCD camera (iXON BV-887, Andor), filter wheel, and z motor (Mac5000, Ludl Electronic Products).
- As our imaging device has an attached auto xy stage , several spheres can be monitored in one assay.
- Device control and image analysis were performed using MetaMorph software .
Induction of WB cells into IPCs
- We designed a differentiation protocol of three basic steps.
- In the first step (chromatin remodeling), WB cells were plated at a density of 2 × 105 per well of 6-well plates in a basal medium containing knockout-serum DMEM and the main components: 1 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 1% non-essential amino acids, 1% B27 supplement, 2 mM L-glutamine, 2% N2 supplement (all from, , ), 20 ng/ml fibroblast growth factor , 20 ng/ml epidermal growth factor , 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 mg/ml STZ .
- Cells were treated with 5 μmol/L (μM) 5-AZA .
- After 48 hours, cells were treated with 100 nmol/L (nM) TSA for 24 hours.
- In the second step (induction and differentiation), basal medium was changed to induction medium containing DMEM with low glucose (1 g/L, , ), 1×ITS , 2 μM RA , and the main components for 7 days.
- In the last step (maturation), the medium was modified from differentiation medium by adding 10 mM nicotinamide without…
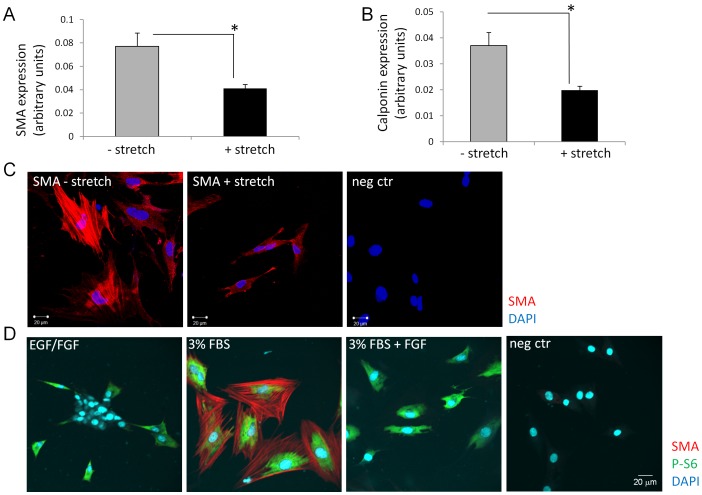
Bladder stretch induced diffusible factors suppress SMC differentiation of SKPs.
- SKPs cultured in medium containing EGF and bFGF were used as control.
Neural stem cell culture
- The generation and differentiation of undifferentiated proliferating cells of the embryonic forebrain were performed as previously described (5 cells/ml into the MHM, which also contained 20 ng/ml EGF and 10 ng/ml bFGF together with 2 µg/ml heparin , and were maintained in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 95% atmospheric air and 5% CO2.
- Fresh media containing 20 ng/ml EGF, 10 ng/ml bFGF and 2 µg/ml heparin were added every other day.
- Cells were cultured for 5–7 days
in vitro (DIV) to form neurospheres. - The neurospheres were enzymatically dissociated and plated onto poly-L-ornithine- and laminin-coated dishes at a density of 3.5×104 cells/cm2 with EGF, bFGF and heparin and then processed further for drug experiments, transfections and immunocytochemistry.
pEGFP-ninein andpEGFP-C1 plasmids were transfected into cells using Lipofectamine 2000 , and microtubule regrowth assays were performed after 24 hours.
Neural stem cell culture
- The generation and differentiation of undifferentiated proliferating cells of the embryonic forebrain were performed as previously described (5 cells/ml into the MHM, which also contained 20 ng/ml EGF and 10 ng/ml bFGF together with 2 µg/ml heparin , and were maintained in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 95% atmospheric air and 5% CO2.
- Fresh media containing 20 ng/ml EGF, 10 ng/ml bFGF and 2 µg/ml heparin were added every other day.
- Cells were cultured for 5–7 days
in vitro (DIV) to form neurospheres. - The neurospheres were enzymatically dissociated and plated onto poly-L-ornithine- and laminin-coated dishes at a density of 3.5×104 cells/cm2 with EGF, bFGF and heparin and then processed further for drug experiments, transfections and immunocytochemistry.
pEGFP-ninein andpEGFP-C1 plasmids were transfected into cells using Lipofectamine 2000 , and microtubule regrowth assays were performed after 24 hours.
Neural stem cell culture
- The generation and differentiation of undifferentiated proliferating cells of the embryonic forebrain were performed as previously described (5 cells/ml into the MHM, which also contained 20 ng/ml EGF and 10 ng/ml bFGF together with 2 µg/ml heparin , and were maintained in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 95% atmospheric air and 5% CO2.
- Fresh media containing 20 ng/ml EGF, 10 ng/ml bFGF and 2 µg/ml heparin were added every other day.
- Cells were cultured for 5–7 days
in vitro (DIV) to form neurospheres. - The neurospheres were enzymatically dissociated and plated onto poly-L-ornithine- and laminin-coated dishes at a density of 3.5×104 cells/cm2 with EGF, bFGF and heparin and then processed further for drug experiments, transfections and immunocytochemistry.
pEGFP-ninein andpEGFP-C1 plasmids were transfected into cells using Lipofectamine 2000 , and microtubule regrowth assays were performed after 24 hours.
2.9. Isolation and Characterization of NCSCs-Like Cells
-
The DPCs were seeded in 6-well plates with an ultralow attachment at a density of 1 × 104 cells/mL in 3 mL of serum-free sphere-forming medium, which consisted of DMEM/F-12 medium (1 : 1), 20 ng/mL bFGF, 20 ng/mL epidermal growth factor (EGF), 1% (
v /v ) N-2 , and 2% (v /v ) B-27. - Two-thirds of the medium was changed every 4 days.
- After culturing for 7 days, sphere numbers were counted under low-power microscope, and the sphere-forming efficiency was expressed as a ratio of spheres to the initial number of single cells.
- Spheres and non-sphere-forming DPCs were separated by filtering through a 40
μ m mesh, followed by adherent culture in proliferation medium. - For measuring the secretion of NTFs with ELISA, the sphere-forming DPCs and total DPCs at the same passage were thoroughly washed with PBS when they had reached ~95% confluence.
- They were then cultured in 5 mL of fresh proliferation medium, and…
Isolation and culture of rat neural stem cells
- Neural stem cells were isolated and cultured as previously described[2 at 37°C.
- The culture medium was changed every 3–4 days.
- After 7 days, mechanically dissociated neural stem cells and undissociated neurospheres were replated in a new culture flask at a density of 1 × 105 cells/mL with fresh culture medium.
Culture of neural stem cells
- Rat pups were disinfected with 75% ethanol and decapitated.
- The isolated hippocampi were diced and triturated using fire-polished Pasteur pipettes.
- The harvested cells were re-suspended and cultured at 2 × 105 cells/mL in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM/F12;, , , ) supplemented with epidermal growth factor (20 ng/mL, , , ), basic fibroblast growth factor (20 ng/mL), and 2% B27 .
- The cells were passaged every 5–7 days, and half volumes of media were replaced every 2–3 days.
- This method of neural stem cell culture is generally accepted and resulted in high-purity neural stem cells[